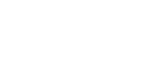Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs - Abdomen
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden) - (Abdomen)
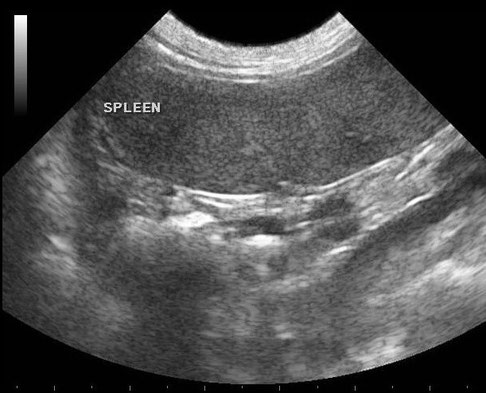
Spleen
(Milz)
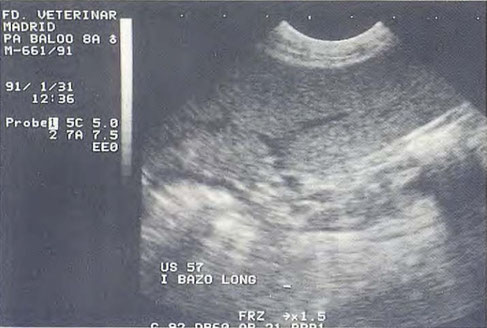
Normal image of a spleen , B = spleen ; SA = acoustic shadow caused by intestinal gas
N. Díez Bru
"Ecografía abdominal en pequeños animales."
CLINICA VETERINARIA DE PEQUEÑOS ANIMALES
Volumen 12, Número 3, Julio/Septiembre 1992

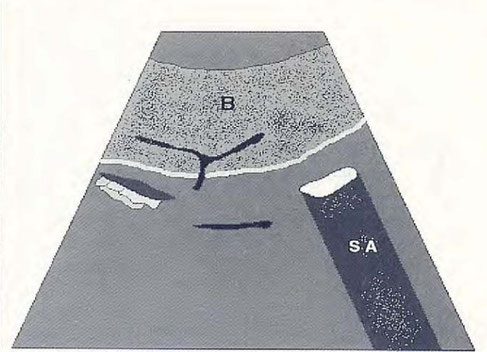
Mass of mixed echogenicity splenic level Histopathological diagnosis : Hematoma spleen
N. Díez Bru
"Ecografía abdominal en pequeños animales."
CLINICA VETERINARIA DE PEQUEÑOS ANIMALES
Volumen 12, Número 3, Julio/Septiembre 1992

Mass (M) of mixed echogenicity that binds normal splenic aparénquima
(E). Histopathological diagnosis : splenic hemangiosarcoma .
N. Díez Bru
"Ecografía abdominal en pequeños animales."
CLINICA VETERINARIA DE PEQUEÑOS ANIMALES
Volumen 12, Número 3, Julio/Septiembre 1992

Ectopic spleen in a dog. A small rounded structure (arrow) is present along the mesenteric side of the spleen, near the hilus. It has similar echogenicity and echotexture as the spleen (Sp). Such tissue may be misinterpreted as an enlarged lymph node or metastatic nodule.
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

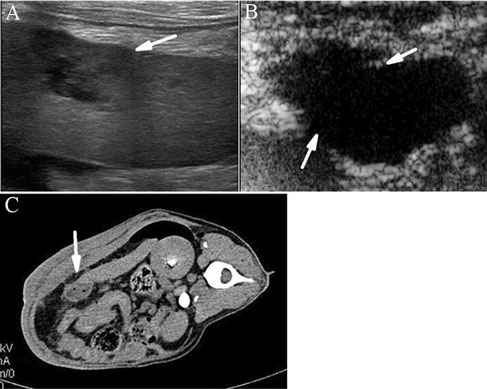
Sagittal ultrasound image of the left cranial abdomen over the palpated mass demonstrating a 10 cm diameter inhomogeneous swelling continuous with the spleen with hypo- and hyperechogenic areas. The surrounding tissue is hyperechogenic.
Authors: Ahmed Abdellatif, Charlotte Günther, Christine Peppler, Martin Kramer
Publication date ( Electronic ): 4 September 2014
Source: PMC ID: 4159529
Journal: BMC Veterinary Research
Publisher: BioMed Central

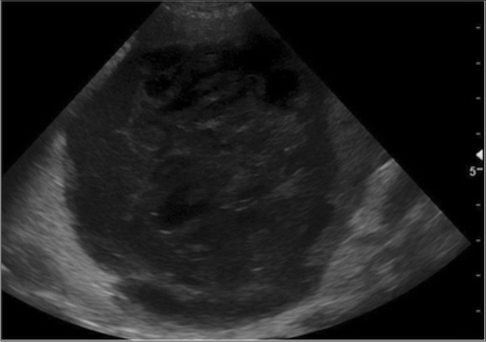
Splenic torsion in a dog
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

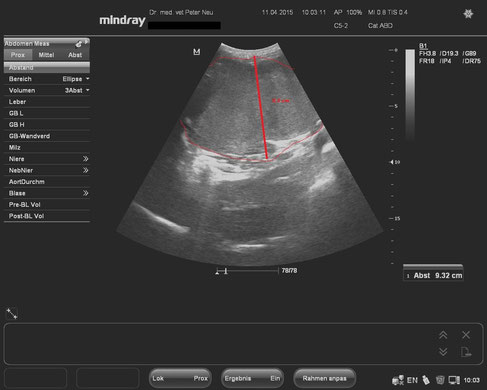
Milztumor mit einer Dicke von 9,3 cm.
Mit freundlicher Genehmigung der Tierarztpraxis Dr. Peter Neu, Coburg.

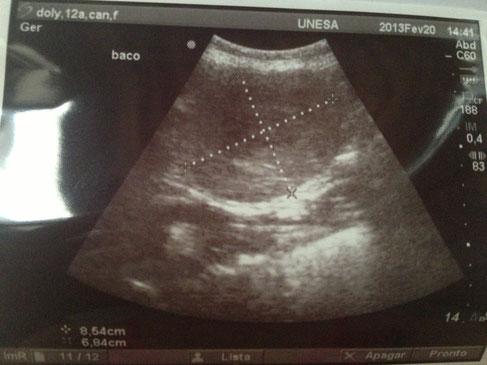
Neoplasia in Spleen.
With special thanks to Priscilla Pinel, Medical Veterinary.
Currently serves in veterinary clinics and homes for the municipality of Rio de Janeiro ( south, north and west ).
http://veterinariapriscillapinel.com.br

Neoplasia in Spleen.
With special thanks to Priscilla Pinel, Medical Veterinary.
Currently serves in veterinary clinics and homes for the municipality of Rio de Janeiro ( south, north and west ).
http://veterinariapriscillapinel.com.br

Image of the spleen from a dog prior to induction of shock. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the spleen indicating the presence of active bleeding, where contrast medium extravasation and pooling (red arrow) were observed.
Qian Lin, Faqin Lv, Yukun Luo, Qing Song, Qinghua Xu, Yihua Su, Yu Tang, Jie Tang
"Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound for Detection of Traumatic Splenic Bleeding in a Canine Model During Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation"
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmu.2013.10.003

Image of the spleen from a dog in traumatic hemorrhagic shock. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the spleen. The splenic lesion appeared as an anechoic perfusion defect area with an unclear irregular border (red arrows), suggesting the absence of active bleeding.
Qian Lin, Faqin Lv, Yukun Luo, Qing Song, Qinghua Xu, Yihua Su, Yu Tang, Jie Tang
"Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound for Detection of Traumatic Splenic Bleeding in a Canine Model During Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation"
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmu.2013.10.003

Image of the spleen from a dog after fluid resuscitation. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the spleen revealing the presence of active rebleeding (red arrow).
Qian Lin, Faqin Lv, Yukun Luo, Qing Song, Qinghua Xu, Yihua Su, Yu Tang, Jie Tang
"Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound for Detection of Traumatic Splenic Bleeding in a Canine Model During Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation"
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmu.2013.10.003

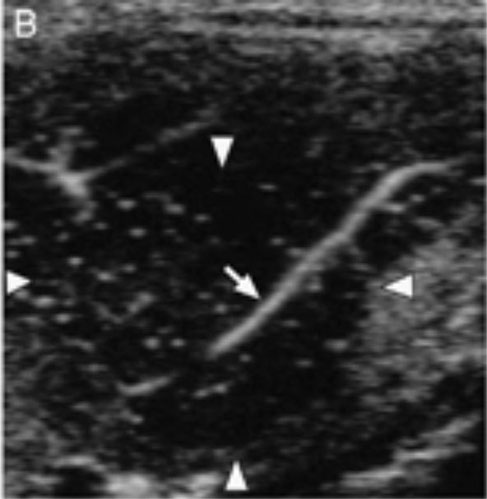
Conventional ultrasound imaging (A) and perflubutane microbubbles-enhanced imagings (B–E) of splenic carcinoma. (B) Immediately after injection, similar pattern vessel was visualized (arrow) in the lesion (arrowheads). (C) During the early vascular phase, the lesion was isoechoic (arrowheads) compared with the surrounding normal parenchyma. (D) During the late vascular phase, the lesion became hypoechoic (arrowheads) compared with the surrounding normal parenchyma. (E) During the parenchymal phase, the lesion was hypoechoic (arrowheads).
Nakamura, K., Sasaki, N., Murakami, M., Bandula Kumara, W.R., Ohta, H., Yamasaki, M., Takagi, S., Osaki, T. and Takiguchi, M. (2010), "Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Characterization of Focal Splenic Lesions in Dogs". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 24: 1290–1297. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2010.0609.x

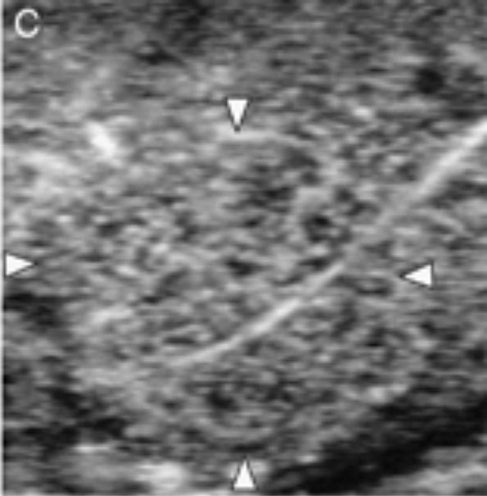
Conventional ultrasound imaging (A) and perflubutane microbubbles-enhanced imagings (B–E) of splenic nodular hyperplasia. (B) Immediately after injection, similar pattern vessel was visualized (arrow) in the lesion (arrowheads). During both (C) the early vascular phase and (D) late vascular phase, the lesion was isoechoic (arrowheads) compared with the surrounding normal parenchyma. (E) During the parenchymal phase, the lesion became hypoechoic (arrowheads).
Nakamura, K., Sasaki, N., Murakami, M., Bandula Kumara, W.R., Ohta, H., Yamasaki, M., Takagi, S., Osaki, T. and Takiguchi, M. (2010), "Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Characterization of Focal Splenic Lesions in Dogs". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 24: 1290–1297. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2010.0609.x

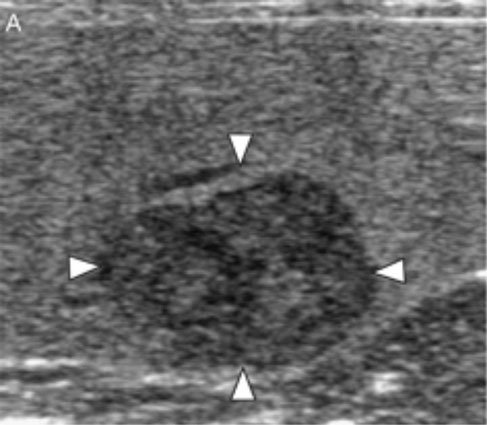
Conventional ultrasound imaging (A) and perflubutane microbubbles-enhanced imagings (B–E) of splenic hematoma. (B) Immediately after injection, no vessel was visualized in the lesion (arrowheads). During both (C) the early vascular and (D) the late vascular phase, the lesion was heteroechoic (arrowheads). (E) During the parenchymal phase, the lesion became hypoechoic (arrowheads).
Nakamura, K., Sasaki, N., Murakami, M., Bandula Kumara, W.R., Ohta, H., Yamasaki, M., Takagi, S., Osaki, T. and Takiguchi, M. (2010), "Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Characterization of Focal Splenic Lesions in Dogs". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 24: 1290–1297. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2010.0609.x

Conventional ultrasound imaging (A) and perflubutane microbubbles-enhanced imagings (B–E) of splenic hemangiosarcoma. During the early vascular phase, (B) the tortuous vessel (arrow) and (C) aberrant wide vessel (arrow) were visualized, but the entire lesion was hypoechoic (arrowheads). (D) During the late vascular phase, the lesion remained hypoechoic (arrowheads) with visualization of vessels (arrow). (E) During the parenchymal phase, the lesion became hypoechoic (arrowheads).
Nakamura, K., Sasaki, N., Murakami, M., Bandula Kumara, W.R., Ohta, H., Yamasaki, M., Takagi, S., Osaki, T. and Takiguchi, M. (2010), "Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Characterization of Focal Splenic Lesions in Dogs". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 24: 1290–1297. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2010.0609.x

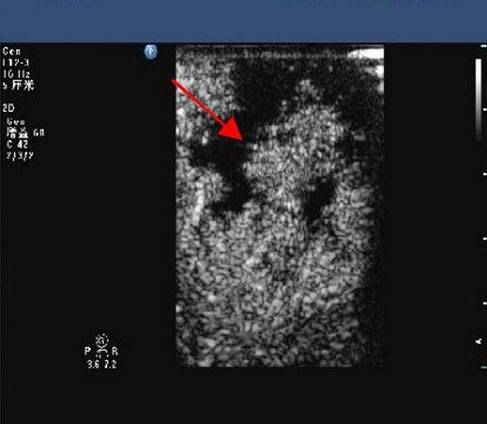
Sonography of the spleen: “lacy parenchyma” (white arrow) and hyperechoic, perivenous triangle (black arrow) with loss of Doppler flow at the hilus.
Flatz K, Blutke A, Berger B, MeyerLinden- berg A and Brühschwein A (2016). "Twisted Fat Stranding in a Dog with Isolated Splenic Torsion Diagnosed with Computed Tomography". M J Vetr 1(1): 003

Observation of hematomas by conventional US, CEUS and CT. (A) Conventional US showed a heterogeneity hypoechoic region in the spleen with a poorly defined margin (white arrow). (B) The hematoma lesions were clearly identified by CEUS, which showed the lesions as anechoic perfusion defects in the arterial, portal, and late phases, lasting approximately 5 min (white arrow). (C) CT examination demonstrated that the volume of the spleen increased with a round or oval shape of a lower density (white arrow).
Tian, J., Xie, X., Lv, F., Yu, T., Wu, R., Zhang, X. ... Tang, J. (2012). Evaluation and establishment of a canine model of delayed splenic rupture using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Molecular Medicine Reports, 6, 483-487. http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.948

Observation of hematomas after rupture by conventional US, CEUS and CT. (A) Conventional US showed a slightly hyperechoic region, with an unclear boundary (white arrow). (B) CEUS showed perisplenic hemoperitoneum, discontinued spleen capsule and the large lamellar and irregular anechoic areas in the parenchyma with a clear margin (white arrow). (C) CT examination showed the irregular and unenhanced areas in the spleen parenchyma with discontinued spleen capsule (white arrow).
Tian, J., Xie, X., Lv, F., Yu, T., Wu, R., Zhang, X. ... Tang, J. (2012). Evaluation and establishment of a canine model of delayed splenic rupture using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Molecular Medicine Reports, 6, 483-487. http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.948

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com